Understanding Type 1 Diabetes
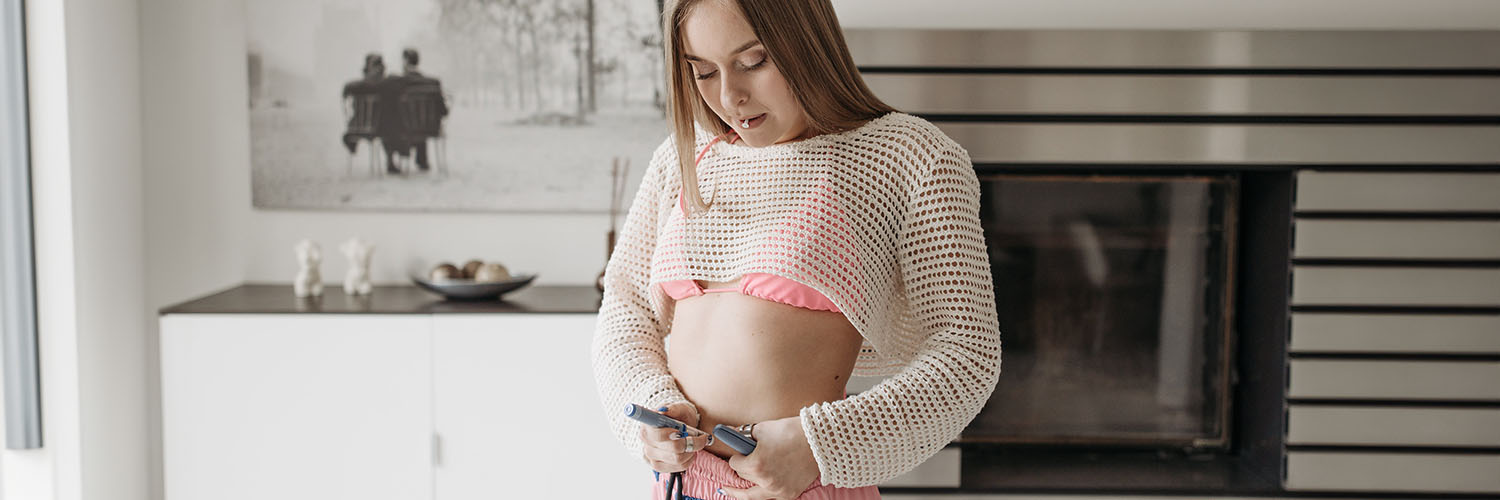
Type 1 diabetes occurs when your body does not produce insulin, a hormone that helps sugar enter your cells to generate energy. Since your body can’t make insulin, it must be replaced through injections or an insulin pump.2
Type 2 diabetes is more common in Australia, with over 1.3 million1 Australians living with it. People with type 2 diabetes can still produce insulin, but their bodies struggle to use it effectively, often requiring medication and/or insulin therapy.2
Keeping Your Blood Glucose Levels in Check
Monitoring blood glucose levels to avoid high or low blood glucose levels is vital to prevent complications and maintain good health. The ideal target range varies, so it’s important to consult your healthcare team.
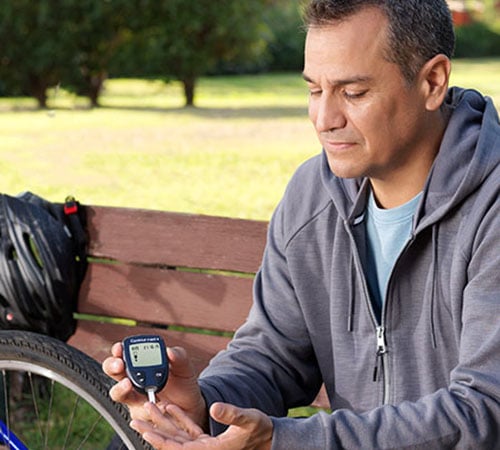
You can check your blood glucose using a blood glucose meter.3 You simply take a drop of blood by finger prick and the meter tells you how much glucose is in your blood at that time. This way, you can check if your blood glucose level is in the healthy range.